Scaling Autonomous Vehicle Data Infrastructure with Apache Hudi at Applied Intuition

Apache Hudi™ at Uber: Engineering for Trillion-Record-Scale Data Lake Operations
From Legacy to Leading: Funding Circle's Journey with Apache Hudi
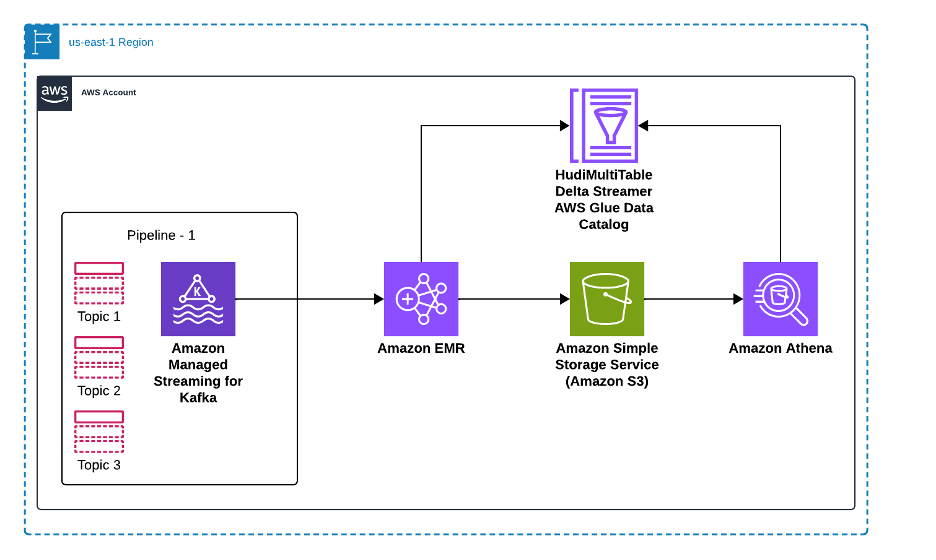
Using Amazon EMR DeltaStreamer to stream data to multiple Apache Hudi tables
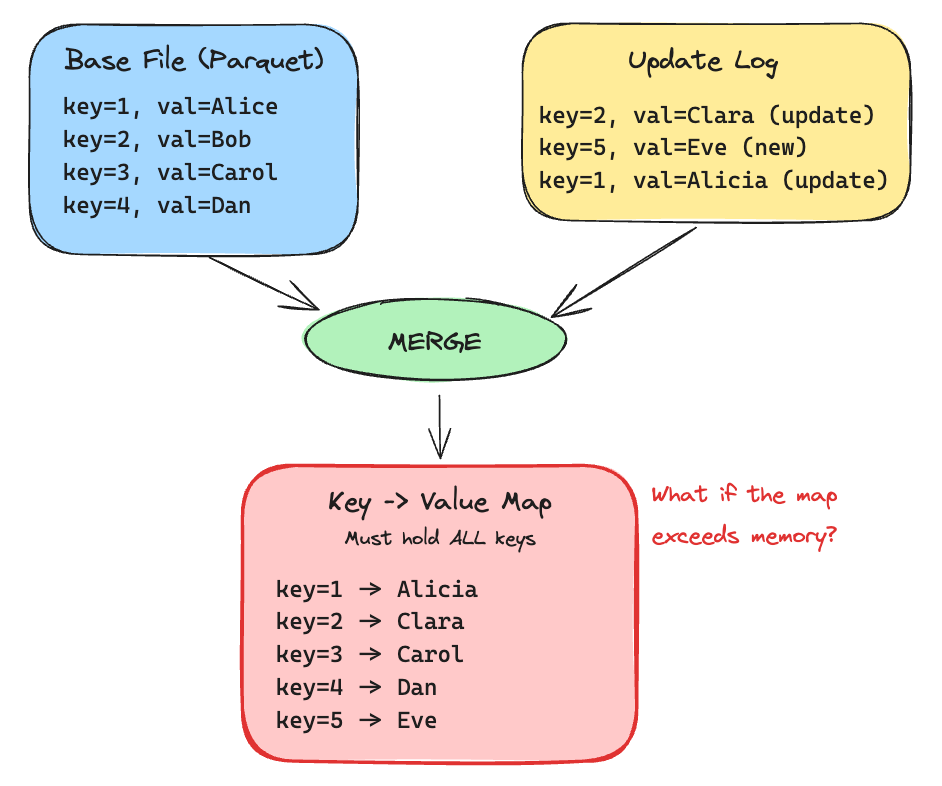
ExternalSpillableMap: Handle Maps Too Big for Memory
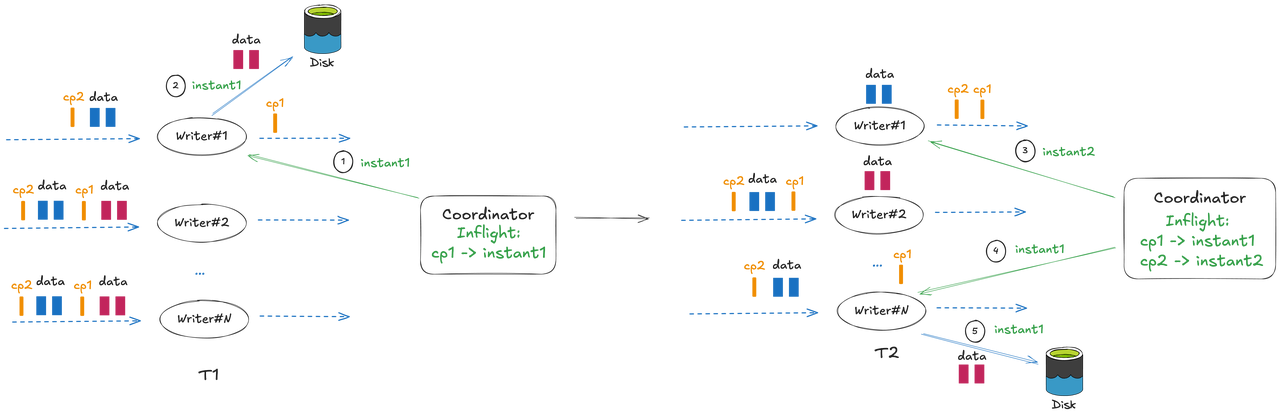
Apache Hudi 1.1 Deep Dive: Async Instant Time Generation for Flink Writers

Apache Hudi 2025: A Year In Review
How Zupee Cut S3 Costs by 60% with Apache Hudi
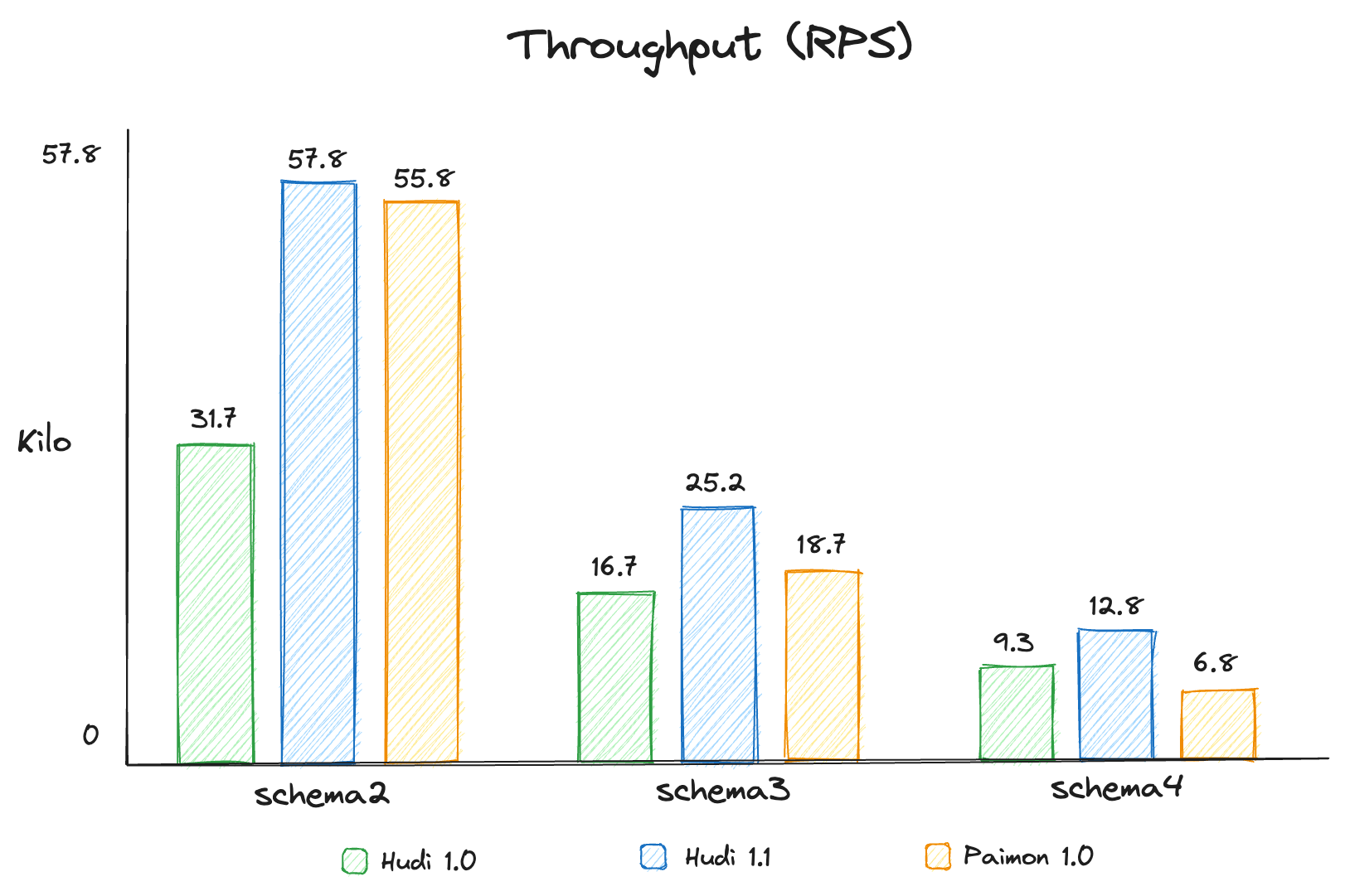
Maximizing Throughput with Apache Hudi NBCC: Stop Retrying, Start Scaling

From Batch to Streaming: Accelerating Data Freshness in Uber's Data Lake
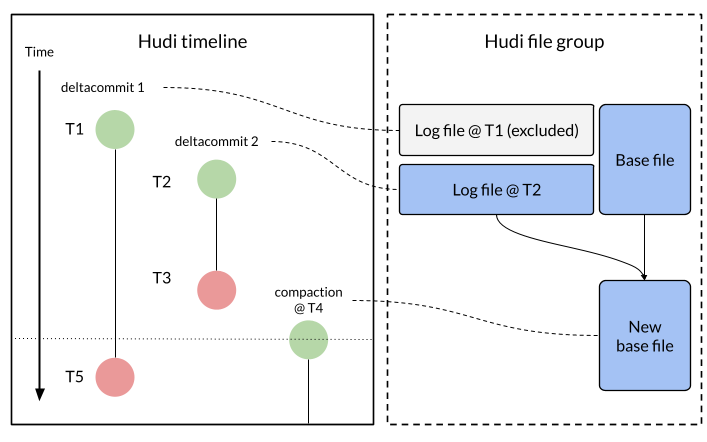
Apache Hudi 1.1 Deep Dive: Optimizing Streaming Ingestion with Apache Flink
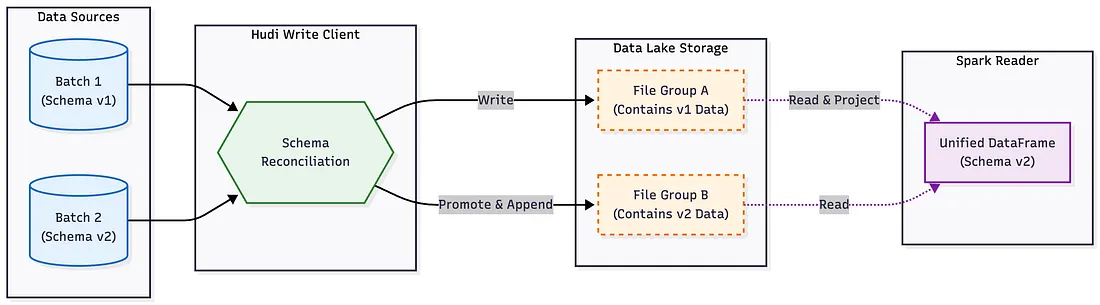
Mastering Schema Evolution with Apache Hudi
Showing 1-12 of 309 posts